
1:16 know what is meant by the terms atomic number, mass number, isotopes and relative atomic mass (Aᵣ).1:15 know the structure of an atom in terms of the positions, relative masses and relative charges of sub-atomic particles.1:14 know what is meant by the terms atom and molecule.1:13 practical: investigate paper chromatography using inks/food colourings.
#GROUP 7 REACTIVITY TREND HOW TO#
1:12 understand how to use the calculation of Rf values to identify the components of a mixture.1:11 understand how a chromatogram provides information about the composition of a mixture.1:10 describe these experimental techniques for the separation of mixtures: simple distillation, fractional distillation, filtration, crystallisation, paper chromatography.1:09 understand that a pure substance has a fixed melting and boiling point, but that a mixture may melt or boil over a range of temperatures.1:08 understand how to classify a substance as an element, a compound or a mixture.1:07 (Triple only) practical: investigate the solubility of a solid in water at a specific temperature.1:06 (Triple only) understand how to plot and interpret solubility curves.1:05 (Triple only) know what is meant by the term solubility in the units g per 100g of solvent.1:04 know what is meant by the terms: solvent, solute, solution, saturated solution.1:03 understand how the results of experiments involving the dilution of coloured solutions and diffusion of gases can be explained.1:02 understand the interconversions between the three states of matter in terms of: the names of the interconversions, how they are achieved and the changes in arrangement, movement and energy of the particles.1:01 understand the three states of matter in terms of the arrangement, movement and energy of the particles.Your answer should include: Diatomic / Poisonous / Green Describe the look and nature of Bromine at room temperature. Your answer should include: Diatomic / Poisonous / Yellow Describe the look and nature of Chlorine at room temperature.
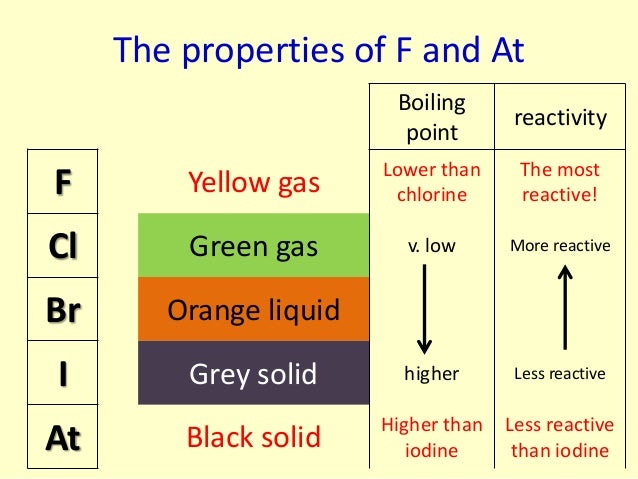
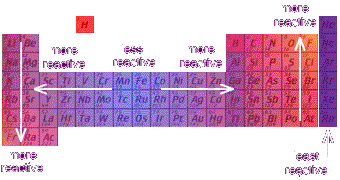
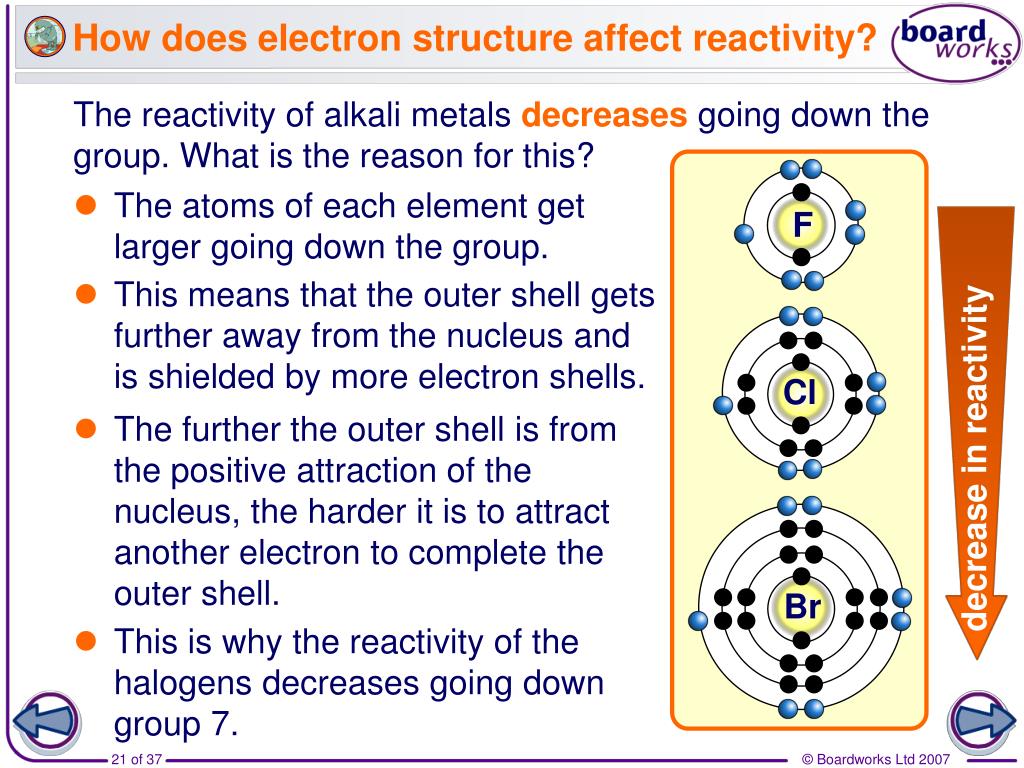
If it is the more reactive molecule that is in the compound, no reaction will occur.ĭescribe the look and nature of Fluorine at room temperature. For example, fluorine will displace chlorine in hydrogen chloride to produce hydrogen fluoride. Displacement Reactionsīe able to work out if a displacement reaction will occur between a halogen compound and a different halogen molecule.īe able to write the equation for any displacement reactions that may occur between halogen compounds and halogen molecules.Ī more reactive halogen will replace another in a compound. The halogen atom takes an electron from metal atom. Halogens form ionic bonds with other metal _atoms _when they react. Halogens form covalent bonds with other non-metal atoms when they react. As you move down the group, the amount of electron shielding increases, meaning that the electron is less attracted to the nucleus. This is because group 7 elements react by gaining an electron. Relative atomic mass increases down the group. This is because the atomic radii increase down the group, increasing the amount of intermolecular forces holding each molecule together. Melting/boiling points increase down the group. For this reason, fluorine is the most reactive halogen and astatine is the least reactive of the halogens. How relative atomic mass increase down group 7 and why.
How melting and boiling points increase down group 7 and why. How group 7 elements react with metals and nonmetals. Group 1Reactions with Metals and Non Metals
They are diatomic (travel in pairs, i.e Br2) Group 7 elements are known as the halogens. Combined Science: Rate of Chemical Change.Combined Science: Atmospheric Chemistry.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
